|
In addition to the basic shape creation and editing functions, users of the Professional grade can keep fillets and chamfer results floating and make post-editing easily by using the NURBS shape. NURBS shapes include "curve" (line shapes), "open surface" (thin shapes), and "closed surface" (manifolds), which can be created and edited from the dedicated toolboxes.
● Toolbox: Create (left) Toolbox: Modify (right)
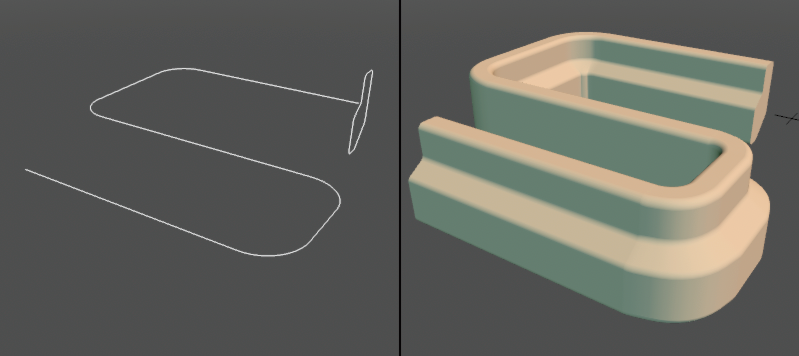
A surface can be created by aligning a curve with another curve.
● Guide curve and a curve to be swept (left) Swept shape (right)
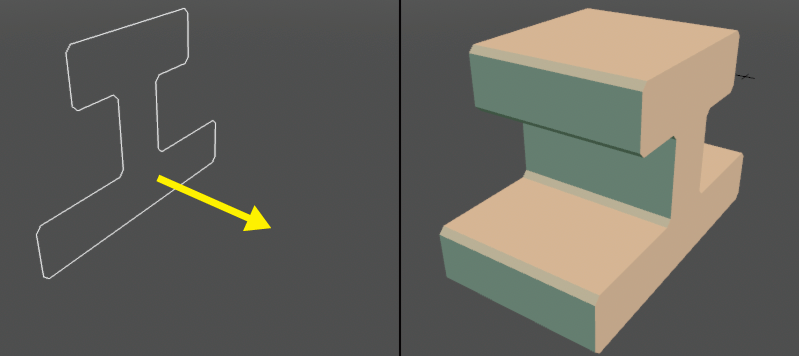
Extrudes a curve in any direction to create a surface.
● Original curve and extrusion direction (left) Extruded shape (right)
Creates a surface by revolving a curve on the specified axis.
● Original curve and rotation axis (left) Shape created by revolving the curve (right)
Creates a mirror image of a shape.
● Original surface (left) Mirror image created in the X direction (right)
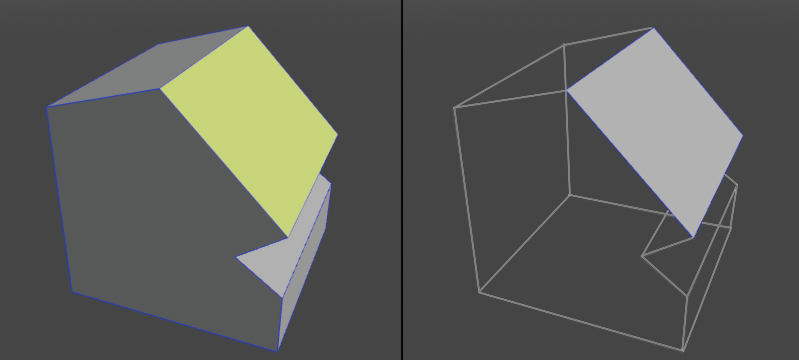
Takes the face of the selected surface out as an open surface.
● Selected face (left) Copied face (right)
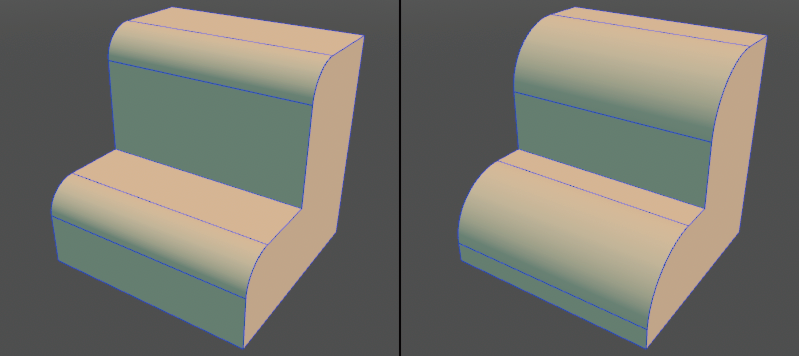
Adds fillet information to the edge. It can be edited later and fixed as a shape depending on the application.
● Fillet set to the edge (left) Specify another value in post-edit (right)
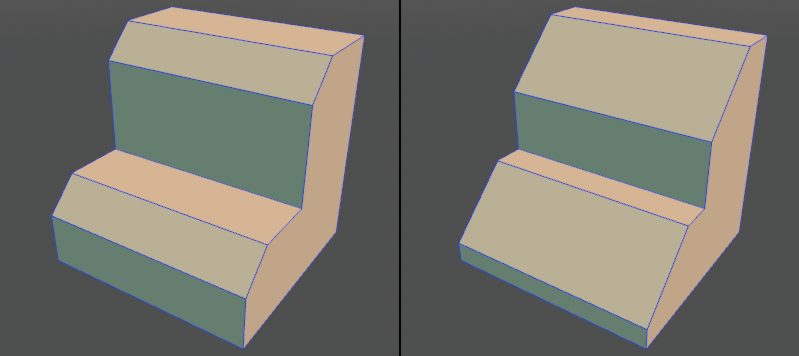
Adds chamfer information to the edges. It can be edited later and fixed as a shape depending on the application.
● Chamfer set to edge (left) Specify another value in post-edit (right)
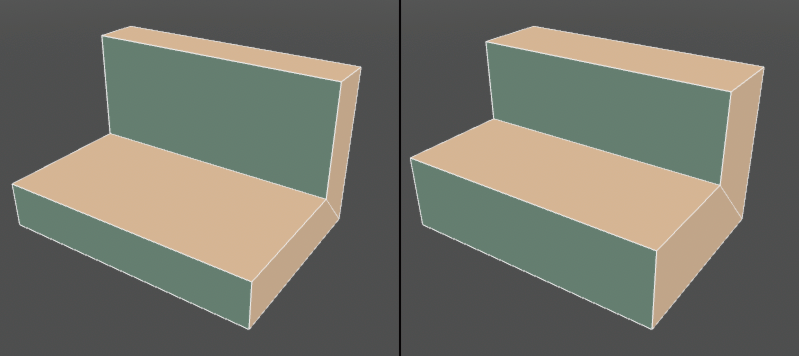
Adds thickness information to the surface. It can be edited later and fixed as a shape depending on the application.
● Thickness set to the surface (left) Specify another value in post-edit (right)
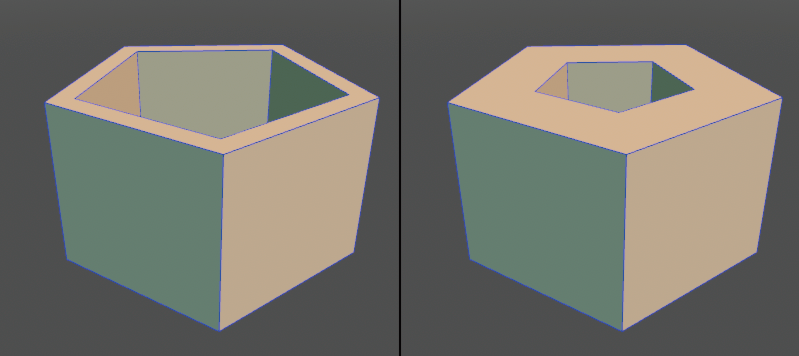
Add shell information to the surface. It can be edited later and fixed as a shape depending on the application.
● Set a shell to the surface (left) Specify another value in post-edit (right)
| Boolean Operation (floating) |
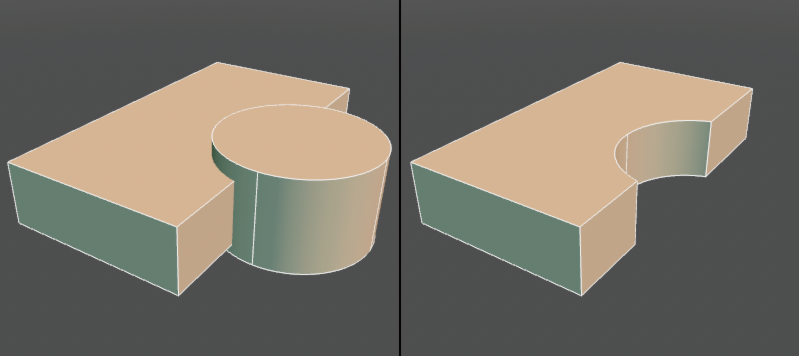
Create a part for doing Boolean operations of "Union", "Difference", and "Intersection". You can move, edit, swap shapes in parts and change operation methods.
● Put the original surface (left) in the Difference Boolean operation part (right)
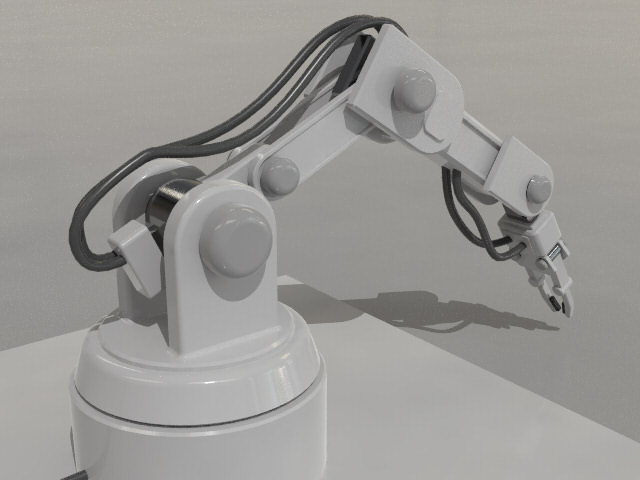
| Example of NURBS Model Creation |
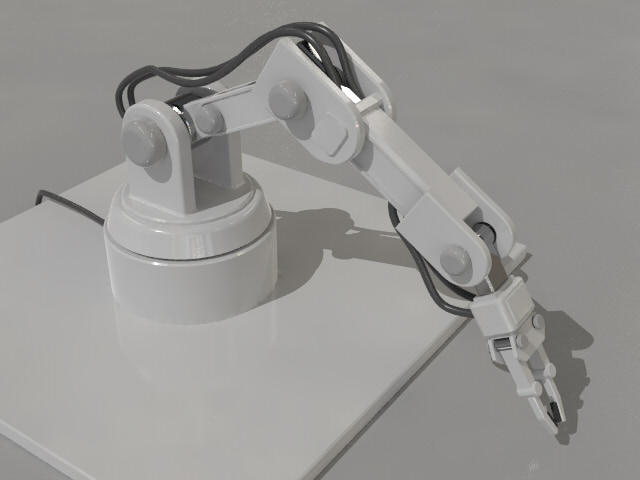
By using these features for modeling, users can create complex models as shown below. You can see the model creation procedure from the Shade3D tutorial "Making a robot arm with NURBS".
Shade3D Tutorial
"Making a robot arm with NURBS" https://tutorials.shade3d.jp/category/%E3%83%AD%E3%83%9C%E3%83%83%E3%83%88%E3%82%A2%E3%83%BC%E3%83%A0%E3%82%92NURBS%E3%81%A7%E4%BD%9C%E3%82%8B
|